- Treatments
- ear, nose & throat infections
- hearing loss
- Surgeries
- myringotomy
- tympanoplasty
- mastoidectomy
- stapedotomy
- FESS
- Tonsillectomy
- Micro laryngeal surgery
- Microscopic & Minimal Invasive Ear Surgery
- Head & Neck
- Head & neck cancer surgeries
- parotid surgery
- thyroid
- salivary glands & laryngeal surgeries
thyroid
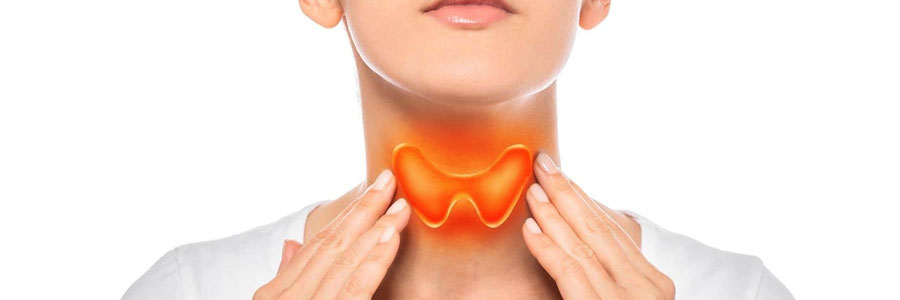
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the lower front part of the neck, just below the Adam's apple. It plays a crucial role in regulating the body's metabolism, energy generation, and overall hormonal balance by producing thyroid hormones.
Functions of the Thyroid
- Thyroxine (T4) and Triiodothyronine (T3): These hormones regulate metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and energy levels.
- Calcitonin: Produced by the C-cells of the thyroid, this hormone helps regulate calcium levels in the blood.
Common Thyroid Disorders
- Thyroid Nodules:
- Benign Nodules: Non-cancerous lumps in the thyroid, often requiring monitoring or biopsy to rule out cancer.
- Malignant Nodules: Cancerous growths that may require surgical removal.
- Goiter: Enlargement of the thyroid gland, which can cause swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing, and breathing issues.
- Thyroid Cancer:
- Types include papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancer.
- Symptoms may include a palpable lump, changes in voice, difficulty swallowing, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Hyperthyroidism:
- Overproduction of thyroid hormones, which can cause weight loss, rapid heartbeat, sweating, and nervousness.
- Conditions like Graves' disease can cause hyperthyroidism.
- Hypothyroidism:
- Underproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and depression.
- Usually managed medically but can require surgical intervention if associated with large goiters or nodules.
Benefits of Thyroid Surgery
- Cancer Treatment: Effective removal of cancerous tissues, potentially curing or controlling the disease.
- Symptom Relief: Alleviates symptoms caused by large goiters or obstructive nodules.
- Diagnostic Clarity: Provides definitive diagnosis and treatment for suspicious nodules.