- Treatments
- ear, nose & throat infections
- hearing loss
- Surgeries
- myringotomy
- tympanoplasty
- mastoidectomy
- stapedotomy
- FESS
- Tonsillectomy
- Micro laryngeal surgery
- Microscopic & Minimal Invasive Ear Surgery
- Head & Neck
- Head & neck cancer surgeries
- parotid surgery
- thyroid
- salivary glands & laryngeal surgeries
salivary glands & laryngeal surgeries
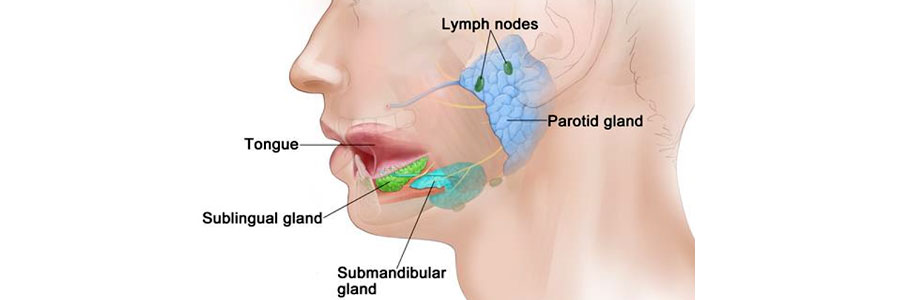
Salivary gland and laryngeal surgeries are specialized procedures performed to address various disorders affecting the salivary glands and the larynx (voice box).
Salivary Glands Surgeries
The major salivary glands include the parotid glands (located in front of the ears), submandibular glands (beneath the jaw), and sublingual glands (under the tongue). These glands produce saliva, which aids in digestion and maintains oral health.
Common Salivary Gland Disorders
- Salivary Gland Stones (Sialolithiasis): Stones blocking the salivary ducts, causing pain and swelling.
- Infections (Sialadenitis): Bacterial or viral infections leading to swelling, pain, and sometimes abscess formation.
- Tumors: Both benign (e.g., pleomorphic adenoma) and malignant (e.g., mucoepidermoid carcinoma) tumors.
- Cysts and Obstructions: Cyst formation or duct obstructions leading to swelling and discomfort.
Types of Salivary Gland Surgeries
- Sialendoscopy: Minimally invasive technique using a small endoscope to diagnose and treat ductal diseases, including stone removal and duct dilation.
- Parotidectomy:
- Superficial Parotidectomy: Removal of the superficial part of the parotid gland, usually for benign tumors.
- Total Parotidectomy: Removal of the entire gland, typically for malignant tumors.
- Submandibular Gland Excision: Removal of the submandibular gland, often for chronic infections, stones, or tumors.
- Sublingual Gland Excision: Removal of the sublingual gland, usually for ranulas (mucus cysts) or tumors.
Laryngeal Surgeries
The larynx, or voice box, is located in the neck and plays a critical role in breathing, voice production, and protecting the airway during swallowing.
Common Laryngeal Disorders
- Vocal Cord Nodules and Polyps: Benign growths causing hoarseness and voice changes.
- Laryngeal Cancer: Malignant tumors affecting the vocal cords, supraglottic (above the vocal cords), or subglottic (below the vocal cords) regions.
- Laryngeal Papillomatosis: Benign tumors caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), leading to voice changes and airway obstruction.
- Vocal Cord Paralysis: Loss of movement in one or both vocal cords, affecting voice and breathing.
Types of Laryngeal Surgeries
- Microlaryngoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure using a microscope and fine instruments to remove small lesions or perform biopsies on the vocal cords.
- Laser Surgery: Uses laser technology to remove lesions, treat early-stage cancers, or perform precise cuts with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
- Partial Laryngectomy: Removal of part of the larynx, typically for cancer, while preserving as much normal function as possible.
- Total Laryngectomy: Complete removal of the larynx, usually for advanced cancer, requiring the creation of a stoma (an opening in the neck) for breathing.
- Vocal Cord Medialization: Procedures to improve voice quality in patients with vocal cord paralysis, including injection laryngoplasty (injecting substances to bulk up the vocal cord) or thyroplasty (surgically repositioning the vocal cord).