- Treatments
- ear, nose & throat infections
- hearing loss
- Surgeries
- myringotomy
- tympanoplasty
- mastoidectomy
- stapedotomy
- FESS
- Tonsillectomy
- Micro laryngeal surgery
- Microscopic & Minimal Invasive Ear Surgery
- Head & Neck
- Head & neck cancer surgeries
- parotid surgery
- thyroid
- salivary glands & laryngeal surgeries
Head & neck cancer surgeries
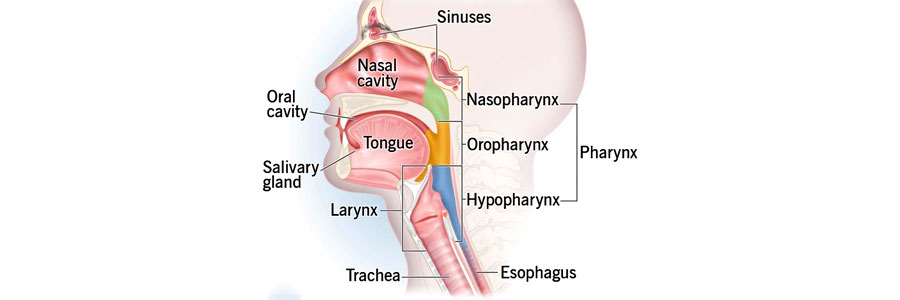
Head and neck cancer surgeries encompass a range of surgical procedures aimed at diagnosing, staging, and treating cancers that occur in the head and neck region.
Types of Head and Neck Cancer Surgeries
1. Diagnostic Procedures:
- Biopsy: Removal of a tissue sample for examination under a microscope to determine if cancer is present and its type.
2. Primary Tumor Resection:
Surgical removal of the primary cancerous tumor in the head or neck region. The specific type of surgery depends on the location and extent of the tumor. Examples include:
- Laryngectomy: Removal of part or all of the larynx (voice box) to treat cancers affecting this area, such as laryngeal cancer.
- Pharyngectomy: Removal of part or all of the pharynx (throat) affected by cancer, including the oropharynx or hypopharynx.
- Maxillectomy: Removal of part or all of the maxilla (upper jawbone) affected by cancer.
- Mandibulectomy: Removal of part or all of the mandible (lower jawbone) affected by cancer.
3. Neck Dissection:
- Removal of lymph nodes in the neck (cervical lymph nodes) to check for the spread of cancer or as a treatment for metastatic cancer.
4. Reconstructive Surgery:
Following tumor removal, reconstructive surgery may be performed to restore the appearance and function of the affected area. This can include:
- Free Flap Reconstruction: Transplantation of tissue from another part of the body (often the forearm, leg, or abdomen) to reconstruct the surgical defect.
- Local Flap Reconstruction: Use of nearby tissue to repair the surgical defect.
5. Salvage Surgery:
- Surgery performed if initial treatments such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy fail to eliminate the cancer or if the cancer recurs after treatment.
Benefits of Head and Neck Cancer Surgeries
- Local Control of Cancer: Surgical removal of the tumor helps to eliminate cancerous cells from the primary site.
- Improved Survival Rates: Early detection and surgical intervention can improve overall survival rates for many types of head and neck cancers.
- Preservation of Function: Surgeons aim to preserve important functions such as speech, swallowing, and breathing whenever possible.
- Comprehensive Treatment: Often part of a multidisciplinary approach that may include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.