- Treatments
- ear, nose & throat infections
- hearing loss
- Surgeries
- myringotomy
- tympanoplasty
- mastoidectomy
- stapedotomy
- FESS
- Tonsillectomy
- Micro laryngeal surgery
- Microscopic & Minimal Invasive Ear Surgery
- Head & Neck
- Head & neck cancer surgeries
- parotid surgery
- thyroid
- salivary glands & laryngeal surgeries
mastoidectomy
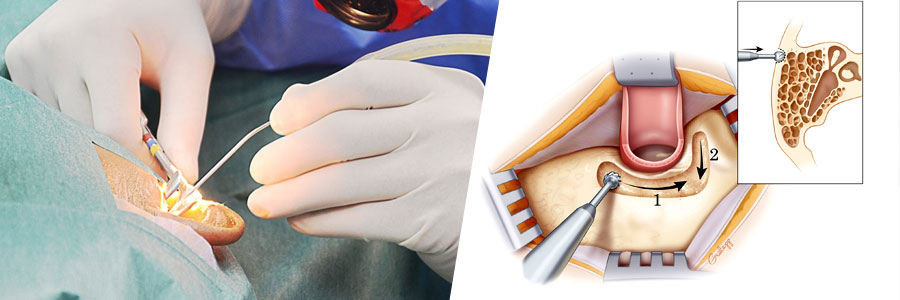
Mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove infected mastoid air cells located in the mastoid bone, which is part of the skull situated behind the ear. This surgery is often necessary to treat severe ear infections that have spread to the mastoid bone or to address complications arising from chronic otitis media, cholesteatoma, or other ear-related conditions.
Indications for Mastoidectomy
- Chronic Otitis Media: Persistent ear infections that do not respond to medical treatment and involve the mastoid bone.
- Cholesteatoma: A benign growth of skin cells in the middle ear that can erode the mastoid bone and other ear structures, leading to hearing loss and infections.
- Mastoiditis: An infection of the mastoid bone following an untreated or severe middle ear infection.
- Complications of Ear Infections: Abscess formation, facial nerve paralysis, or infections spreading to the brain (e.g., meningitis).
- Tumors: Benign or malignant tumors in the mastoid region.
Benefits of Mastoidectomy
- Elimination of Infection: Removes the source of infection, thereby preventing its spread and recurrence.
- Prevention of Complications: Reduces the risk of serious complications such as brain abscess, meningitis, or facial nerve damage.
- Improved Hearing: In some cases, hearing can be preserved or improved, especially when combined with tympanoplasty.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Reduces chronic ear discharge and pain, leading to better overall health and quality of life.
Prevention of Conditions Leading to Mastoidectomy
- Prompt Treatment of Ear Infections: Treating ear infections early and thoroughly to prevent them from spreading to the mastoid bone.
- Vaccinations: Ensuring children receive recommended vaccines to reduce the risk of ear infections.
- Avoiding Ear Trauma: Preventing damage to the ear that could lead to infections or complications.