- Treatments
- ear, nose & throat infections
- hearing loss
- Surgeries
- myringotomy
- tympanoplasty
- mastoidectomy
- stapedotomy
- FESS
- Tonsillectomy
- Micro laryngeal surgery
- Microscopic & Minimal Invasive Ear Surgery
- Head & Neck
- Head & neck cancer surgeries
- parotid surgery
- thyroid
- salivary glands & laryngeal surgeries
stapedotomy
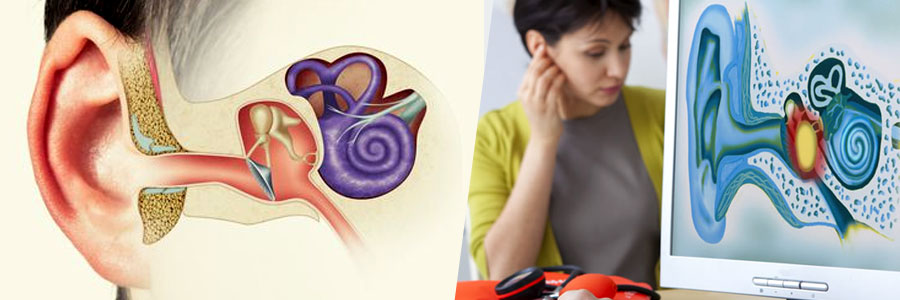
Stapedotomy is a microsurgical procedure performed to treat hearing loss caused by otosclerosis, a condition in which abnormal bone growth around the stapes bone in the middle ear interferes with its ability to transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear. This surgery involves creating a small opening in the stapes footplate and inserting a prosthetic device to bypass the immobilized stapes, thereby restoring the transmission of sound.
Indications for Stapedotomy
- Otosclerosis: The primary indication for stapedotomy is otosclerosis, which leads to progressive conductive hearing loss due to the fixation of the stapes bone.
- Conductive Hearing Loss: Hearing loss that results from an inability of the middle ear structures to transmit sound effectively to the inner ear, particularly when it does not respond to medical treatment.
Benefits of Stapedotomy
- Improved Hearing: Most patients experience a significant improvement in hearing, with some achieving near-normal hearing levels.
- Quality of Life Enhancement: Restored hearing can improve communication abilities, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure is relatively quick, often completed in less than two hours, and typically involves minimal discomfort and a short recovery period.
Prevention of Conditions Leading to Stapedotomy
While otosclerosis is largely hereditary and not preventable, general ear health practices can help maintain overall ear function:
- Regular Hearing Check-Ups: Early detection of hearing changes can prompt timely intervention.
- Avoiding Loud Noises: Protecting ears from excessive noise exposure can prevent other types of hearing loss.
- Good Nutrition: A balanced diet supports overall health, including bone health.